Extracellular Vesicles
Ascites-derived EVs – An isolation approach using free-flow electrophoresis
Abstract
Although extracellular vesicles (EVs) have been characterized to some extent and a wide variety of purification techniques have been described, the separation of EVs from other extracellular particles remains challenging, especially for primary bioliquids such as ascites or blood plasma. As a novel approach for purifying EVs from primary biofluids, we used free-flow electrophoresis (FFE), a well-established matrix-free, liquidbased, highly versatile technology for separating analytes according to their net charge.
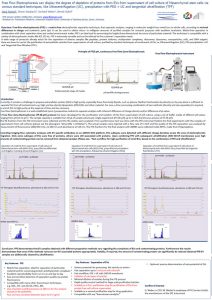
Free Flow Electrophoresis can display the degree of depletion of proteins from EVs from supernatant of cell culture of Mesenchymal stem cells via various standard techniques, like Ultracentrifugation (UC), precipitation with PEG + UC and tangential ultrafiltration (TFF)
Abstract
A Free Flow Zone Electrophoresis (FF-ZE-pH) protocol has been developed for the purification and isolation of EVs from supernatant of cell culture, using a set of buffer media of different pH-values ranging from pH 4.6 to pH 7.
According imaging flow cytometry analyses with EV specific antibodies on an AMNIS ISXII platform, EVs subtypes were detected with different charge densities across the area of electrophoretic migration. Only some subtypes of EVs were free of proteins, others were still associated with proteins. Upon combining FFE with subsequent ultrafiltration (300 KD-UF-membranes) even high amounts of contaminating protein can be removed from obtained samples.
FFE demonstrates that EV samples obtained with different preparation methods vary regarding the complexity of EVs and contaminating proteins. Furthermore, the results demonstrates that none of the methods removes non-EV associated proteins appropriately. Notably, if required, the amount of contaminating protein can significantly be reduced obtained FFE-EV samples are additionally cleaned by ultrafiltration.
Identifying extracellular vesicle subpopulations by Free Flow Electrophoresis
Abstract
Extracellular vesicle (EV) driven cellular exchange plays an important role in maintaining normal bodily homeostasis. Charge is known to be one of the important factors influencing EV uptake by the receiving cell and EV charge arises from their expression of different surface molecules like proteins, lipids and glycans. Here we describe a standard workflow to identify differently charged EV populations by Free flow electrophoresis (FFE), which is typically used for the separation of various and complex protein mixtures. First, FFE Quality Control (QC) was done by performing two electrophoretic pre-tests to confirm the quality of discrimination of ionic analytes, followed by an additionalperformance test in order to test the quality and reproducibility of electrophoretic separation. After passing all QC tests, we used FFE to separate purified EVs derived from SK-MEL-37 cells, a melanoma cell line.
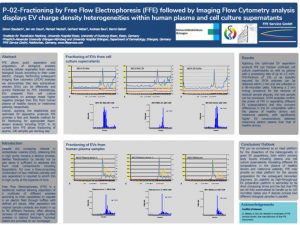
P-02-Fractioning by Free Flow Electrophoresis (FFE) followed by Imaging Flow Cytometry analysis displays EV charge density heterogeneities within human plasma and cell culture supernatants
Abstract
FFE allows quick separation and preparation of biological analytes including cellular organelles from various biological liquids according to their outer electric charges. Performing subsequent imaging flow cytometry (IFCM) analyses we demonstrate that also extracellular vesicles (EVs) can be effectively and quickly fractioned by FFE. Interestingly, EVs prepared from cell culture supernatants on average reveal higher negative charges than EVs from human plasma of healthy donors or melanoma patients, respectively.
Overall, applying the established and optimized EV separation protocols FFE provides a fast and feasible method for EV fractioning for appropriate down-stream analysis including IFCM. In its current form FFE allows fractioning of approx. 100 samples per working day.
P-03-Free-flow electrophoresis provides a new and effective way of isolating extracellular vesicles from plasma and ascites
Abstract
The combination of Free Flow Electrophoresis (FFE) as a separation technique and AMNIS as an analytical technique can display differences in charge density of extracellular vesicles (subfractions), as we have already shown previously. Here in addition we use Nano Flow Cytometry (NanoFCM) to further characterize EV derived from various bio fluids (plasma, ascites) isolated using FFE. FFE can offer various separation protocols, differing in the distance of electrophoresis or time of electrophoresis. The separation protocol with a prolonged distance of electromigration was elected for these experiments.
P-04-Free Flow Electrophoresis (FFE) enables subfractionation of human plasma-derived exosomes (EV) from blood samples of healthy donors.
P-05 Free flow electrophoresis setup and experimental workflow for the separation of extracellular vesicles from human plasma
The complete workflow of start-up of FFE-instrument prior the experiment for the enrichment of exosomes from melanoma plasma sample